Home »
Scala
The while loop in Scala
By IncludeHelp Last updated : October 10, 2024
While loop
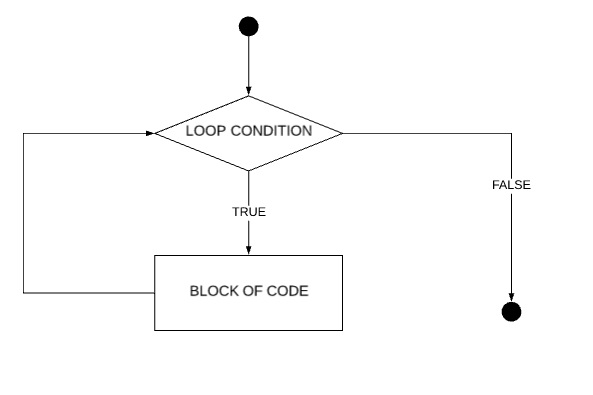
The while loop in Scala is used to run a block of code multiple numbers of time. The number of executions is defined by an entry condition. If this condition is TRUE the code will run otherwise it will not run.
The while loop is used when the program does not have information about the exact number of executions taking place. The number of executions is defined by an entry condition that can be any variable or expression, the value evaluated in TRUE if it's positive and FALSE if it's zero.
This loop might not run even once in the life span of code. If the condition is initially FALSE. The flow will not go in to loop in this case.
The while loop is also called entry controlled loop because its condition is checked before the execution of the loop's code block.
Syntax of while loop
while(condition){
//Code to be executed...
}
Flow chart
Example of while loop
object MyClass {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
var myVar = 2;
println("This code prints 2's table upto 10")
while(myVar <= 10){
println(myVar)
myVar += 2;
}
}
}
Output
This code prints 2's table upto 10
2
4
6
8
10
Code explanation
The above code is to explain the usage of while loop in Scala. In this code, we have used a variable named myVar that is used as a counter in while loop. For printing text, to the screen, we are using println method that moves the cursor to the next line after printing. We have used += assignment operator that we have learned previously. The code prints that table of 2 up to 10.
From this section, I am going to give you assignments that you can complete and submit to know your progress.
Assignment 1 (difficulty - beginner): Print all numbers from 100 - 399 that are divisible by 3. (use while loop and functions.)
Assignment 2 (difficulty - intermediate): Print all number between 541 - 643 that have 3, 5 and 7 as a factor.
Advertisement
Advertisement