Home »
Interview coding problems/challenges
All Root to Leaf Paths
All Root to Leaf Paths: In this article, we are going to see how to print all root to leaf paths?
Submitted by Radib Kar, on March 25, 2019
Problem statement
Given a Binary Tree of size N, write a program that prints all the possible paths from root node to the all the leaf node's of the binary tree.
Example:
Let's the tree be like following:
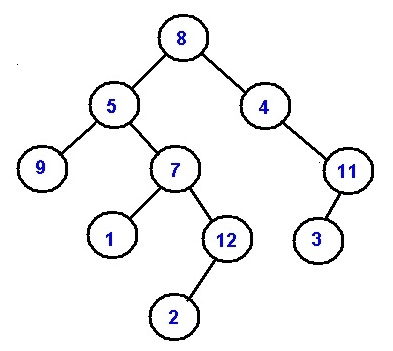
All possible root to leaf paths in this tree is:
8->5->9
8->5->7->1
8->5->7->12->2
8->4->11->3
Solution:
To print all the root to leaf paths we have used recursive approach.
The idea is to maintain a list of nodes on the paths and to print the list while leaf node is reached.
Algorithm:
Pre-requisite:
Input binary tree root, list a
FUNCTION printpathrecursively(Node* current_node, list a){
1. base case
IF(current_node ==NULL)
return;
END IF
2. append current_node ->data to the list;
IFcurrent_nodeis leaf node //leaf node reached
Print the list; //printing the root to leaf path
END IF
3. printpathrecursively(current_node->left,a);//recur for left subtree
printpathrecursively(current_node->right,a);//recur for right subtree
END FUNCTION
In the main function create an empty list a, And call printpathrecursively(root, a);
Example with explanation:

Nodes are represented by their respective values.
In main we call printpathrecursively(root, a)
----------------------------------------------
printpathrecursively(8, a)
current node not NULL
append 8 to list a
list: 8
current node is not leaf node
call to printpathrecursively(8->left, a)
call to printpathrecursively(8->right, a)
----------------------------------------------
printpathrecursively(8->left, a):
=printpathrecursively(5, a)
current node not NULL
append 5 to list a
list: 8,5
current node is not leaf node
call to printpathrecursively(5->left, a)
call to printpathrecursively(5->right, a)
----------------------------------------------
printpathrecursively(5->left, a):
=printpathrecursively(9, a)
current node not NULL
append 9 to list a
list: 8,5, 9
current node is leaf node
Print the list
call to printpathrecursively(9->left, a)
call to printpathrecursively(9->right, a)
call to printpathrecursively(9->left, a)
----------------------------------------------
=printpathrecursively(NULL, a)
current nodeNULL
control return to FUNCTION printpathrecursively(9, a)
At printpathrecursively(9, a)
call to printpathrecursively(9->right, a)
----------------------------------------------
=printpathrecursively(NULL, a)
current node NULL
control return to FUNCTION printpathrecursively(9, a)
At printpathrecursively(9, a)
Control reaches end of the void function
Thus control returns to the calleefunction printpathrecursively(5, a)
printpathrecursively(5->right, a):
----------------------------------------------
=printpathrecursively(7, a)
current node not NULL
append 7 to list a
list: 8, 5, 7 //Don’t think list will be 8, 5, 9, 7.
List at this function was 8, 5 not 8, 5, 9
//List has not been passed by referenced
current node is not leaf node
call to printpathrecursively(7->left, a)
call to printpathrecursively(7->right, a)
This can be carried out until control gets back to main
which called function printpathrecursively(root, a)
You can do rest by your own to have much more clear idea about how the program is actually working.
C++ Implementation
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//tree node
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
};
void print(vector<int> a){
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
if(i==a.size()-1)
cout<<a[i];
else
cout<<a[i]<<"->";
}
}
void printpathrecursively(Node* root,vector<int> a){
if(root==NULL) //base case
return ;
a.push_back(root->data);
if(!root->left && !root->right){ //leaf node reached
print(a);
cout<<endl;
}
printpathrecursively(root->left,a);//recur for left subtree
printpathrecursively(root->right,a);//recur for right subtree
}
void printPaths(Node* root)
{
vector<int> a;
printpathrecursively(root,a);
}
//creating new nodes
Node* newnode(int data){
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
int main() {
//**same tree is builted as shown in example**
cout<<"tree in the example is build here"<<endl;
//building the tree like as in the example
Node *root=newnode(8);
root->left= newnode(5);
root->right= newnode(4);
root->right->right=newnode(11);
root->right->right->left=newnode(3);
root->left->left=newnode(9);
root->left->right=newnode(7);
root->left->right->left=newnode(1);
root->left->right->right=newnode(12);
root->left->right->right->left=newnode(2);
cout<<"Printing all root to leaf paths......"<<endl;
printPaths(root);
return 0;
}
Output
tree in the example is build here
Printing all root to leaf paths......
8->5->9
8->5->7->1
8->5->7->12->2
8->4->11->3
Advertisement
Advertisement