Home »
DBMS
DBMS SQL Joins (with Examples)
DBMS SQL Joins: In this tutorial, we will learn about the different types of joins with their examples (using SQL Queries).
By Shamikh Faraz Last updated : May 28, 2023
A SQL Join statement is used to join rows as well as data from two or more tables. This combination is based on a common field between them.
Types of SQL Joins
- Inner Join
-
Outer Join
- Left Join / Left Outer Join
- Right Join / Right Outer Join
- Full Join
Sample Tables
Tables, which we are going to use in this tutorial


1. Inner Join
INNER JOIN joins both the tables. This selects all rows from both the tables. This keyword will combine columns values of both the tables based on join predicate. Join predicate normally we can call the same column data in both tables like above both tables are having ‘Roll No.’ column in same. This will be join predicate. Join will continue as long as the join predicate satisfies.

Syntax
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.common_column = table2.common_column;
table1: Student_table
table2: Course_table
join predicate: Roll No.
Code to Join
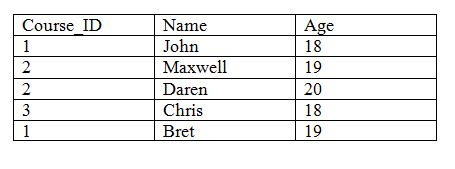
SELECT Course_table.COURSE_ID, Student_table.NAME, Student_table.AGE
FROM Student_table
INNER JOIN Student_table
ON Student_table.ROLL_NO = Course_table.ROLL_NO;
Output
2. Outer Join
This is of three types.
2.1. Left Join/ Left Outer Join
LEFT OUTER JOIN performs a join starting with the first (left-most) table and then any matching second (right-most) table records. This join gives a result set of all the rows of the left table and matching rows from the right table. If there are no matching rows on right side, this gives null. This is also called left join.

Syntax
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1,
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
table1: Student_table
table2: Course_table
join predicate: Roll No.
Code to Join
SELECT Student_table.NAME, Course_table.COURSE_ID
FROM Student_table
LEFT JOIN Course_table
ON Course_table.ROLL_NO = Student_table.ROLL_NO;
Output

2.2. Right Join / Right Outer Join
Right Outer JOIN performs a join starting with the second/right table and then any matching second from first/left table. This join gives a result set of all the rows of the second/right table and matching rows from the first/left table. If there are no matching rows on left first/left side, this gives null. This is also called right join.

Syntax
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1,
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
table1: Student_table
table2: Course_table
join predicate: Roll No.
Code to Join
SELECT Student_table.NAME, Course_table.COURSE_ID
FROM Student_table
RIGHT JOIN Course_table
ON Course_table.ROLL_NO = Student_table.ROLL_NO;
Output

2.3. Full Join
FULL JOIN joins both LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN. The result will contain all the records from both the tables. If there is no matching record, there will be NULL values.

Syntax
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1,
FROM table1
FULL JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
table1: Student_table
table2: Course_table
join predicate: Roll No.
Code to Join
SELECT Student_table.NAME, Course_table.COURSE_ID
FROM Student_table
FULL JOIN Course_table
ON Course_table.ROLL_NO = Student_table.ROLL_NO;
Output

Advertisement
Advertisement