Home »
Data Structure
Find largest subtree sum in a tree
In this article, we are going to see how we can find the largest subtree sum in the given tree?
Submitted by Radib Kar, on September 12, 2020
Prerequisite: Transform to sum tree
In this article, we are going to see how we can find the largest subtree sum in a tree?
In the below example,

The largest subtree sum is 11 for the subtree rooted by 13.
One thing is if all nodes are positive valued then, of course, the entire tree will have the largest sum tree sum which is basically the sum of all the nodes.
But since there can be nodes with negative values too, that's why we can't take the entire subtree and need to check for all subtree sum. Of course, the brute force method is to find subtree sum rooted by each node and to take the maximum sum. But the complexity would be O(n^2).
So the efficient approach is a recursive solution using postorder traversal which will solve in one pass. The algorithm is below:
We have a variable ans which returns the ultimate result and initialized as INT_MIN.
The recursive function is like below:
FUNCTION maxSubtreeSumRecur(node, ans){
If node is NULL
return 0;
node value is transformed to the subtree sum
rooted by the node recursively
Update the ans with updated node value
if that's greater than ans
return updated node value;
END FUNCTION
So it's actually a postorder traversal which return the subtree sum and we update ans if needed.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// tree node is defined
class TreeNode {
public:
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int data)
{
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
int maxSubtreeSumRecur(TreeNode* node, int& ans)
{
if (!node)
return 0;
node->val += maxSubtreeSumRecur(node->left, ans) + maxSubtreeSumRecur(node->right, ans);
ans = max(ans, node->val);
return node->val;
}
int maxSubtreeSum(TreeNode* root)
{
int ans = INT_MIN;
if (!root)
return 0;
maxSubtreeSumRecur(root, ans);
return ans;
}
int main()
{
//building the tree like the example
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(-10);
root->left = new TreeNode(7);
root->right = new TreeNode(13);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(-4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->right->left = new TreeNode(5);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(-7);
cout << "Maximum subtree sum is: " << maxSubtreeSum(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Maximum subtree sum is: 11
Dry Run:
Since it's a postorder traversal we will show the dry run in bottom-up fashion as the recursion will reach there first before returning something.

Figure 1: root->val -4 and subtree sum both 0, so total sum -4

Figure 2: root->val 3 and subtree sum both 0, so total sum 3

Figure 3: root->val 7 and subtree sum -4+3, so total sum 6
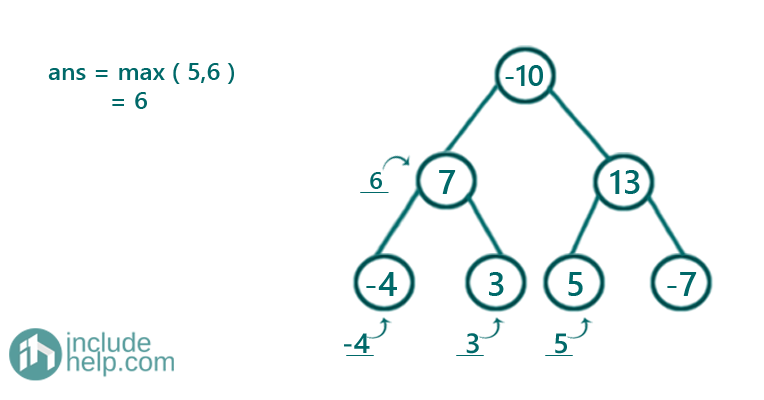
Figure 4: root->val 5 and subtree sum 0, so total sum 5

Figure 5: root->val -7 and subtree sum 0, so total sum -7

Figure 6: root->val 13 and subtree sum 5+(-7), so total sum 11
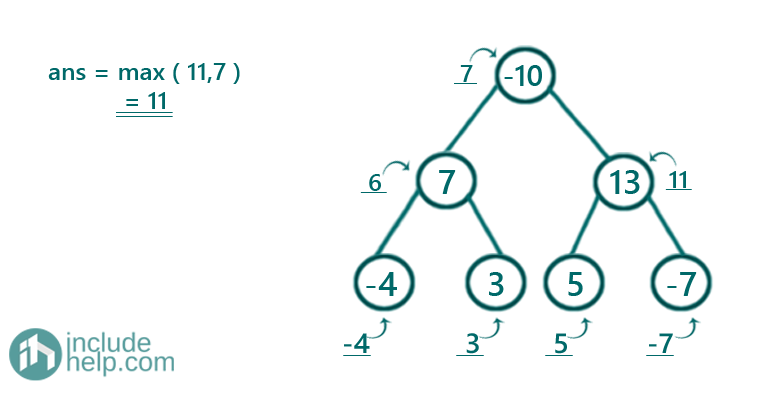
Figure 7: root->val -10 and subtree sum 6+11, so total sum 7
Thus the largest subtree sum is 11 which appeared in Figure 6
Advertisement
Advertisement