Home »
Data Structure
Deletion in Binary Search Tree (BST)
Deletion in Binary Search Tree: Here, we will learn how to delete a Node in Binary Search Tree. In this article you will find algorithm, example in C++.
Submitted by Abhishek Jain, on July 29, 2017
Suppose, T is a binary Search tree, and an ITEM of information is given. This section gives an algorithm which deletes ITEM from the tree T.
The deletion operation first uses Search () to check for node N which contains ITEM is present in the tree or not. The way N is deleted from the tree depends primarily on the number of children of node N. There are three cases:
Case I:
N (node) has no children. Then N is deleted from T by simply replacing the location of N in the parent node by the NULL pointer.
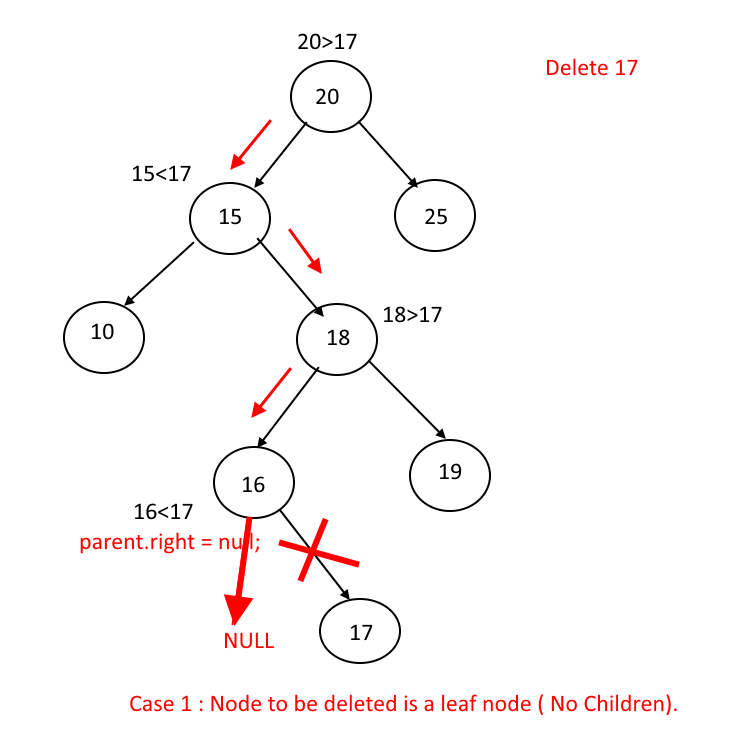
Reference: algorithms.tutorialhorizon.com/binary-search-tree-complete-implementation/
Case II:
N has exactly one child. Then N is deleted from T by simply replacing the location of N in parent node by the location of the only child of N.

Reference: algorithms.tutorialhorizon.com/binary-search-tree-complete-implementation/
Case III:
N has two children. Then N is deleted from T by replacing its location in parent node with its selected child node, selection is possible in two different ways:
- Find the in-order successor of node N (smallest node in the right subtree of the node N).
- Find the in-order predecessor of Node N (largest node in the left subtree of the node N).
Note: To better understand about in-order successor and in-order predecessor please go through the link: (Find In-Order Successor and predecessor in Binary Search Tree).

Reference: algorithms.tutorialhorizon.com/binary-search-tree-complete-implementation/
Consider the C++ program:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool c=false;
struct node
{
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
struct node* getNode(int data)
{
node* newNode=new node();
newNode->data=data;
newNode->left=NULL;
newNode->right=NULL;
return newNode;
}
void inorder(struct node* root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
inorder(root->left);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
inorder(root->right);
}
}
node* findMin(node*root)
{
while(root->left!=NULL)
{
root=root->left;
}
return root;
}
struct node* Insert(struct node* root, int data)
{
if (root == NULL)
return getNode(data);
if (data < root->data)
root->left = Insert(root->left, data);
else if (data > root->data)
root->right = Insert(root->right, data);
return root;
}
bool Search(node*root,int value)
{
if(root==NULL)
return false;
else if(root->data == value)
{
return true;
}
else if(value < root-> data)
Search(root->left,value);
else if(value > root->data)
Search(root->right,value);
}
node* Delete( node* root,int value)
{
c=Search(root,value);
if(root==NULL)
return root;
else if(value< root->data)
{
root->left= Delete(root->left,value);
}
else if(value> root->data)
{
root->right= Delete(root->right,value);
}
// Node deletion
else
{
//case 1: Leaf Node
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)
{
delete root;
root=NULL;
return root;
}
//case 2: one child
else if(root->left==NULL)
{
struct node* temp=root;
root=root->right;
delete temp;
return root;
}
else if(root->right==NULL)
{
struct node* temp=root;
root=root->left;
delete temp;
return root;
}
//case 3: 2 child
else
{
struct node*temp=findMin(root->right);
root->data=temp->data;
root->right=Delete(root->right,temp->data);
}
}
return root;
}
int main()
{
node* root=NULL;
root=Insert(root,20);
Insert(root,15);
Insert(root,25);
Insert(root,18);
Insert(root,10);
Insert(root,16);
Insert(root,19);
Insert(root,17);
cout<<"Before Deletion: "<<endl;
cout<<"Inorder: ";
inorder(root);
cout<<endl<<endl;
Delete(root,15);
if(c)
{
cout<<"Node Deleted"<<endl;
cout<<"\nAfter Deletion: "<<endl;
cout<<"Inorder: ";
inorder(root);
cout<<endl;
}
else
cout<<"Node Not Found"<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Before Deletion:
Inorder: 10 15 16 17 18 19 20 25
Node Deleted
After Deletion:
Inorder: 10 16 17 18 19 20 25
Advertisement
Advertisement