Home »
Computer Network
Optical Fiber (Fiber Optics) in Computer Network
Computer Network | Optical Fiber (Fiber Optics): In this article, we are going to study about Optical Fiber. We will first define the term Optical Fiber and describe its propagation modes. We will also discuss it's the types of Step Index Multimode fiber and Graded Index Multimode fiber and will also discuss its advantages and disadvantages and illustrate it with a diagram.
By Monika Jha Last updated : May 05, 2023
What is Optical Fiber (Fiber Optics)?
It is made up of glass or plastic and transmits signals in the form of light. To understand Optical Fiber, we first need to explore several aspects of the nature of the light.
Propagation Modes
Current technology supports two methods along optical channels for propagating light, each requiring fiber with different physical characteristics:
- Multimode
- Single Mode
Multimode can be implemented in two forms:
- Step- Index
- Graded- Index
1) Multimode
It is named as Multimode fiber cause of multiple beams from a light source move through the core in different paths. These beams travel within the cable in a way depends on the structure of the core.
1.1. Multimode Step-Index
In multimode step-index fiber, from the center to the edges the density of the core remains constant. A beam of light travels through this constant density in a straight line until it reaches the interface of the core and the cladding.
At the interface, there is an abrupt change to a lower density that modifies the angle of the beam’s motion. The suddenness of this change is referred to by the term step-index.
This figure shows various beams (or rays) traveling through a step-index fiber. Some beams in the middle go through straight lines by the core and reach the destination without reflecting or refracting.

Some beams strike the interface of the core and cladding at that angle which is smaller than the critical angle. These beams penetrate the cladding and are lost. Still, others hit the edge of the core at angles greater than the critical angle and reflect into the core and off the other side, bouncing back and forth down the channel until they reach the destination.
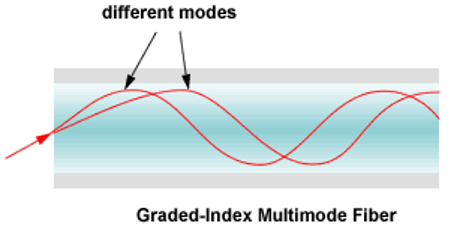
1.2. Multimode Graded-Index
The second type of fiber called multimode graded-index fiber decreases the distortion of the signal through the cable. The word index here refers to the index of refraction and the index of refraction is related to density.
A graded-index fiber, therefore, is one that varying densities. Density is highest al the center of the core and decreases gradually to its lowest at the edge.
This figure shows the impact of this variable density on the propagation of light beams.
2) Single Mode
The single-mode uses step-index fiber and a highly concentrated on the source of light which limits beams to a small range of angles, all close to the horizontal. It is manufactured with a much smaller diameter than that of multimode fibers and with substantially lower density (index of refraction).
The decrease in density of beams results in a critical angle that is close enough to 90 degrees to make the propagation of beams almost horizontal.
In this case, the propagation of different beams is almost identical and delays are negligible. All of the beams arrive at the receiver’s side together and can be recombined without distortion to the signal.

Advantages of Fiber Optics
The following are the advantages of fiber optics
- Noise resistance.
- This transmission does not use electricity but it uses light. Noise is not a factor. The only possible interference is External light which is blocked from the channel by the outer jacket.
- Less signal attenuation: The distance of Fiber-optic transmission is significantly greater as compared to other guided media. A signal can go through for miles without requiring regeneration.
- Higher bandwidth: As compared to coaxial cable or twisted-pair cable, the fiber-optic cable can support dramatically higher bandwidths that increase data rates. There is a limitation on data rates and bandwidth utilization over fiber-optic cable and not by the medium but by the signal generation and reception technology available.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optics
The following are the disadvantages of fiber optics
- Cost: This cable is expensive as any impurities or imperfections in the core can throw off the signal, manufacturing must be painstakingly precise. Also, a laser light source can cost thousands of dollars, compared to hundreds of electrical signal generators.
- Installation/maintenance: If there is any roughness or cracking in the core of an optical cable diffuses light and modifies the signal. All connections must be perfectly aligned and matched for core size and must provide a completely light-tight seal. Metallic media connections, on the other hand, can be made by cutting and crimping using relatively unsophisticated tools.
- Fragility: Glass fiber can be easily broken than wire, making it less useful for applications where hardware portability is required.
Advertisement
Advertisement