Home »
Java programming language
How to access MetaData Of a class using Java?
In this article, we are going to learn that how can we access metadata of a class using java? MetaData of a class includes the class name, fields name, methods, constructor etc.
By Jyoti Singh Last updated : March 23, 2024
Access MetaData of a Java Class
To get the MetaData, we use Java reflection API. Java refractor class provides the methods to get the metadata of a class.
Methods to Access MetaData of a Java Class
Here, we are going to use the following methods:
- class.forName()
This method loads a class which is provided as the parameter , if class is not found it will throw an error.
- isInterface()
This function checks whether a class is an interface or not and returns a Boolean value.
- getDeclaredFields()
This returns all fields name of a class.
- getDeclaredMethods()
This returns all methods name of a class.
- getDeclaredConstructor()
This returns all constructor name of a class.
Java Program to Access MetaData of a Java Class
Let's understand them more clearly by this example. Here, we have a class name Product with three fields in it and an interface named NoteBook.
package logicProgramming;
/*
* In This Program We are Going to Get Meta Data Of Running Class
* And Going To Examine And Change The Behavior Of Class
*/
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//an interface
interface NoteBook {
int bookId = 100;
}
//a class
class Product {
private int productId;
private String name;
public long price;
//constructor
public Product(int productId, String name, long price) {
this.productId = productId;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
//constructor
public Product() {}
//this function prints the data of the object
public void putProduct() {
System.out.println("ProductId :" + this.productId + "\nName :" + this.name + "\nPrice" + this.price);
}
public String toString() {
return ("ProductId :" + this.productId + "\nName :" + this.name + "\nPrice" + this.price);
// to return object so that object values are printed rather
//than it's hexadecimal address
}
}
//main class
public class ExClassMetaData_ReflectionAPI_JAVA {
public static void main(String arg[]) {
try {
//Class.forName(ClassName) Use For Loading The Class
Class cs = Class.forName("logicProgramming.Product");
System.out.println(cs.getName()); //getName() function is getting the name of the class
//getClass() Is also used To get The meta Data Of Class
System.out.println();
Product P = new Product();
Class pcls = P.getClass(); //getting the meta data of Product class
System.out.println(pcls.getName());
System.out.println();
//public boolean isInterface() tells that whether
//the current class is Interface or a Simple Class
System.out.println(Class.forName("logicProgramming.Product").isInterface());
//Book Is a Interface so It Will print True...
System.out.println();
System.out.println(Class.forName("logicProgramming.NoteBook").isInterface());
//public Field[] getDeclaredFields()
//returns an array of name of all fields of this class.
Field fields[] = cs.getDeclaredFields();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Fields Of product Class");
//loop to print the fields name of the class
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
System.out.println(fields[i]);
}
//public Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
//returns an array of name of all methods of this class.
Method methods[] = pcls.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Methods Of product Class");
//loop to print the methods name of the class
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
System.out.println(methods[i]);
}
//public Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors()
//returns the total number of constructors of this class.
Constructor < Product > constructors[] = pcls.getDeclaredConstructors();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Constructors Of product Class");
//loop to print the constructor name of the class
for (int i = 0; i < constructors.length; i++) {
System.out.println(constructors[i]);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output
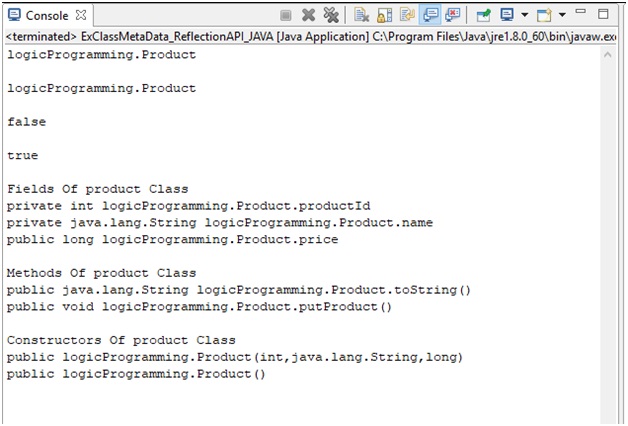
Here, we have all the meta data of the class.
Note: "logicProgramming" is the name of the package , replace it with your package name
Advertisement
Advertisement