Home »
XML Tutorial
XML Introduction
By IncludeHelp Last updated : December 25, 2024
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a markup language designed to store and transport data in a human-readable and machine-readable format. It is widely used for data representation and exchange across various platforms and systems.
Key Features of XML
- Structured Data: Organizes data into a tree-like structure.
- Self-Descriptive: Tags provide information about the data.
- Platform Independent: Works across different platforms and systems.
- Extensible: Allows users to define custom tags.
Basics of XML Syntax
XML documents are composed of elements, attributes, and a prolog. Let's look at the basic structure:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bookstore>
<book>
<title>Learning XML</title>
<author>Jane Doe</author>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book>
<title>Mastering XML</title>
<author>John Smith</author>
<price>39.99</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
Output
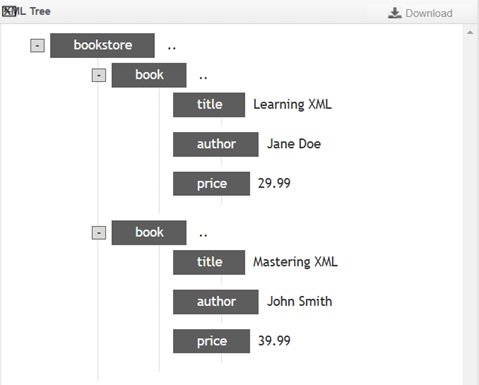
Explanation
-
Prolog:
- The first line: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- Defines the XML version and character encoding.
-
Root Element:
- <bookstore> is the root element that encapsulates all other elements.
-
Child Elements:
- <book>, <title>, <author>, and <price> are nested elements.
-
Text Content:
- Text values are enclosed within tags (e.g., <title>Learning XML</title>).
-
Closing Tags:
- Every opening tag (e.g., <title>) must have a corresponding closing tag (e.g., </title>).
Rules of XML
-
Well-Formed XML:
- XML documents must have a single root element.
- All tags must be properly nested and closed.
- Attribute values must be quoted.
-
Case Sensitivity:
- XML tags are case-sensitive (<book> is different from <Book>).
-
No Reserved Keywords:
- Custom tags can be created, but they must not conflict with reserved characters (<, >, &).
-
White Spaces:
- XML preserves white spaces, which can be used for formatting.
XML vs HTML
|
Aspect
|
XML (eXtensible Markup Language)
|
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
|
|
Purpose
|
Designed to store and transport data.
|
Designed to display data in a web browser.
|
|
Tag Definition
|
Custom tags can be created by the user.
|
Predefined set of tags for web content.
|
|
Structure
|
Strictly structured and follows a tree-like hierarchy.
|
Loosely structured; not all tags require closing.
|
|
Case Sensitivity
|
Tags are case-sensitive (e.g., <Tag> ≠ <tag>).
|
Tags are not case-sensitive (e.g., <h1> = <H1>).
|
|
Closing Tags
|
Every opening tag must have a closing tag.
|
Some tags (e.g., <img>, <br>) do not require closing.
|
|
Validation
|
Can be validated using DTD or XSD.
|
No strict validation mechanism.
|
|
Focus
|
Data-centric.
|
Presentation-centric.
|
|
Attributes
|
Attributes are used sparingly; data is stored in elements.
|
Attributes are widely used to define element behavior.
|
|
Whitespace Handling
|
Whitespace is preserved.
|
Whitespace is generally ignored by the browser.
|
|
Use Cases
|
Data storage, configuration files, web services (e.g., SOAP).
|
Web page creation, user interface development.
|
|
Extensibility
|
Fully extensible; users define their own structure.
|
Limited extensibility; fixed structure.
|
|
Parsing
|
Requires explicit parsing using XML parsers.
|
Directly rendered by web browsers.
|
|
Error Handling
|
Errors must be corrected for the XML document to be valid.
|
Browsers can ignore minor errors and display content.
|
|
Data Exchange
|
Suitable for exchanging data between applications.
|
Not suitable for data exchange; used for display only.
|
Advantages of XML
- Data Exchange: XML simplifies data sharing between systems.
- Human Readability: The structure is easy to understand and edit.
- Customizable: Users can define their own tags and structure.
Applications of XML
- Web Services: Used in SOAP and REST APIs.
- Data Storage: Formats like RSS and Atom use XML.
- Configuration Files: Many software applications use XML for configuration.
Advertisement
Advertisement